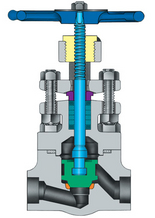
Forged Steel Globe Valve
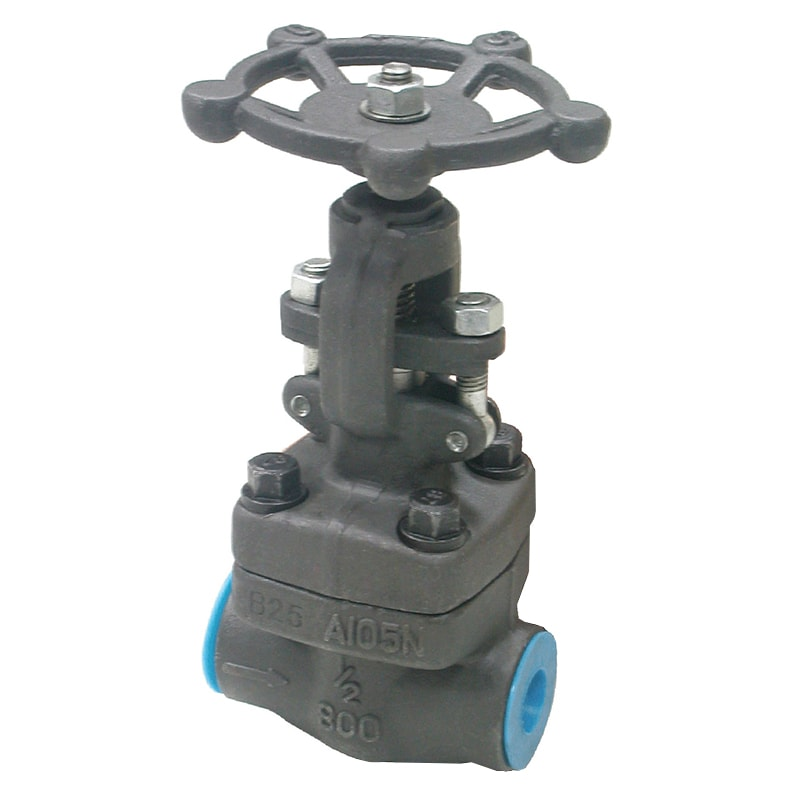

Features and benefits
● A compact but extremely sturdy design for high pressure-temperature service.
● Available types: Stop, Stop check, Needle, Flow control.
● Available with bolted or welded bonnet.
● Packing rings are pre-compressed to 4000 psi to provide a high integrity seal.
● Repairable 2-piece stem drive.
● Available with double packing, leak-off connection, and live-loading.
NPS 1/4 – 2 (DN 8 – 50)
Pressure rating
ASME Class 150 – 1500
Standard connections
Threaded, Socket weld, Flanged
Globe Valve BS 1873 and API 602
What is a globe valve? When shall it be used instead of gate and ball valves? In this article, we illustrate the scope of this type of valve (which is, in a word, to regulate the flow), the differences with other types of valves, the alternative designs, and specifications (BS 1873 for the cast steel and API 602/BS 5352 for the forged steel type).
GLOBE VALVE USES
Globe valves are used to regulate the flow of a fluid and to shut-off the fluid (even if ball valves and gate valves are always preferred for shut-off operations). Globe valves are bi-directional valves, differently from check valves, meaning that the fluid can flow either way within the valve.
The image illustrates how the valve works and its main components: the flow is managed via a disc that can be lifted (manually or via actuators) from the seat, thus regulating the volume of the allowed flow.

The key specifications for globe valves used for piping applications in the petrochemical industry are:
- BS 1873: cast steel valves
- API 603: stainless steel valves
- API 602/BS 5352: forged steel valves
- API 598 and BS EN 12266-1: valves testing
- ASME B16.10: face to face dimensions for valves
- ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47: flanged connections
- ASME B16.25: butt weld connections design
- ASME B16.34: pressure and temperature ratings by material grade
GLOBE VALVE ADVANTAGES AND Disadvantages The advantages are:
- Good throttling and shut-off capabilities
- Easy to maintain and resurface the seats
- Can be used as a stop-check valve in case the disc is not attached to the stem
The main disadvantages are:
- the valve creates a pressure drop in the piping system (different from gate valves): this is since the flow of the fluid is not linear inside the valve, which has an “S-shaped” passageway (see the image below)
- shut-off requires more torque than gate valves

GLOBE VALVE TYPES
The valve is available in three main types, considering the shape of the body:
- straight or “T” type
- angle or “90 degrees”
- Y pattern or “wye globe valve”

The globe valve symbol in P&ID diagrams is the following: ![]()
GLOBE VALVE VS BALL VALVE
The key difference between a globe and a ball valve is that a ball valve is designed for shut-off operations, whereas a globe valve is designed to throttle fluids. These two valves are industry-standards respectively for shut-off (ball valve) and for regulation (globe valve) applications.
A globe valve does not fit shut-off operations, due to the pressure drop it creates in the piping system (a problem that does not exist for full bore ball valves).
Ball valves have a long service life even in case of continuous on-off operations; globe valves would deteriorate easily under this type of service.
GLOBE VALVE VS GATE VALVE
The main differences between these two valves are:
- fluid shut off is the main goal of gate valves, whereas flow throttling is the main goal of globe valves
- gate valves have poor, to none, fluid regulation capacity
- gate valves do not generate a pressure drop in the pipeline, globe valves do
- globe valves open faster than gate valves
Concluding on this topic: use a ball valve (or a gate valve) for shut-off operations; use a globe valve for regulation. Do not consider these valves as interchangeable.

GLOBE VALVE DIAGRAM
A general assembly drawing for globe valves is shown in the image:

Nonetheless, a large number of variations exist, depending on the following factors:
- body material: cast (BS 1873) and forged (API 602/BS 5352)
- bonnet design: standard or pressure seal type (for high-pressure applications)
- bonnet to body connection: bolted or welded
- valve end connections type: flanged (as shown in the image), buttweld, socket weld/threaded (forged bodies)
- disc type
- stem type (rising/non-rising)
- seal type: conical or flat
- specification: BS, API, EN
- type of actuation: manual, with a gearbox, with an actuator
